AUTOMATING ENCRYPTION AND DECRYPTION
Introduction
Defense
That’s the tactic organisations and their IT teams need to take against cybersecurity threats. Taking defensive, proactive steps, long before a data breach or misuse of your sensitive data, helps shield against potential incidents that can wreak havoc with budgets, reputations, and resources. One such move is the implementation of encryption and decryption of data.
What is Encryption?
Encryption is a method of encoding data (messages or files) so that it is unusable or unreadable null it is decrypted. With encryption in place, only authorized pares with keys can read or access that data. Crypton uses Crypton setoff rules, to scramble the data being sent. Once received, the data can be decrypted using the key provided by the message originator.
The effusiveness of any given encryption technology is determined by the strength of the algorithm, the length of the key, and the appropriateness of the encryption system selected.
Because key, and key, and to an unauthorized party, the informant remains private and confidential, whether being transmitted or stored on a system. Unauthorized pares will see nothing but an unorganized assembly of system. Unauthorized technology can provide assurance of data integrity as some algorithms offer protection against forgery and tampering. The ability of the technology to protect the protect the that the encryption and decryption keys be properly managed by authorized pares.
How it works:
Not every message or piece of data is for everyone’s eyes. That’s the basic premise of why organizations need encryption. But how does it work? Do you need different types of encryption for different situations? Can encryption be integrated with your existing business technology? Let’s take a look
Unlocking encryption keys
There are two types of cryptographic key systems essential to encryption technology, symmetric and asymmetric.
Symmetric key system:
This is also known as a secret key system. With this system, all parties have the same key. The keys can be used to encrypt and decrypt messages and must be kept secret or the security is compromised. For the parties to get the same key, there must be a way to securely distribute the keys. While this can be done, the security controls needed can make this system impractical for widespread and commercial use on an open network like the Internet.
Asymmetric key system:
This system, also known as a public/private key done, the problem of distributing the keys used in the symmetric key system. Two keys are used in this system. One key is kept secret, or “private, “while the other key is made widely available to anyone that needs it and is referred to as the “public key.” The private and public keys are mathematically related so that information encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted by the corresponding private key.

Encryption terms to know
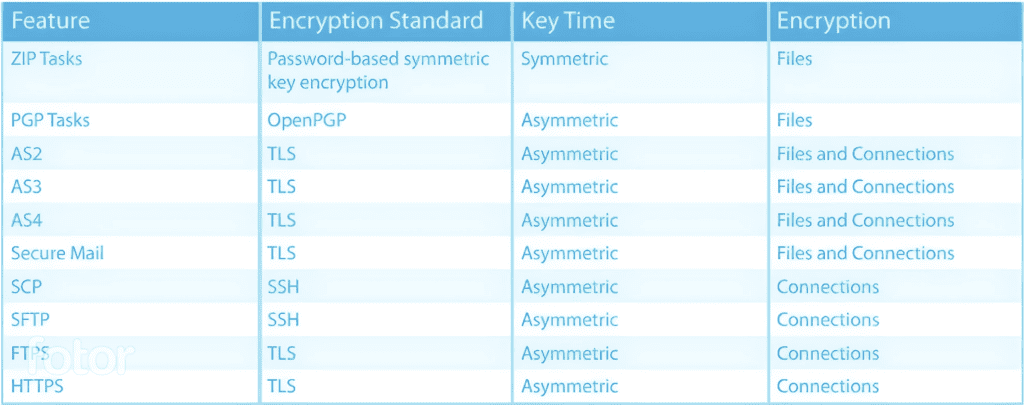
AES: Short for Advanced Encryption Standard. It is a popular encryption standard that is approved by the NIST.
Algorithm: Also known as ciphers, algorithms are the rules or specific instructors for the encryption process. Triple DES, RSA, and AES are examples of algorithms, or ciphers.
Ciphertext: The result of encryption performed on plaintext using an algorithm, known as a cipher.
Decryption: The process of converting unreadable cipher text to readable informant.
Email Encryption: Email encryption can secure email online via a number of options using encryption. These include TLS, password, push/pull, S/MIME, and PGP encryption.
Encryption: The science of protecting informant by transforming it into a secure format.
Key: A randomized strong of bits used to encrypt and/or decrypt data. Each key is unique, and longer keys are harder to break. Common key lengths are 128 and 256 bits for private keys and 2048 bits for public keys.
PGP: Short for Prey Good Privacy. PGP is an encryption program that provides cryptographic privacy and encryption for data communication.

Why does encryption matter?
Encryption matters because cybersecurity threats exist and are continually growing in number. In addition, inadvertent data leaks from internal staff are also responsible for nearly half of all data loss incidents. Also, many industries such as banking, healthcare and more, require encryption to ensure compliance requirements are met.
Locking data down and away from both deliberate, malicious threats, as well as from accidental mishandling, is your best protection from the huge financial toll a data breach can have on your organizing, along with loss of reputing and trust from trading partners and more.
Data needs to be safely encrypted both while it is in transfer or transit to an intended recipient and while it is arrests as while stored on a server. Doing so is one of the most important processing your cybersecurity arsenal, and for good reason: it’s your last line of defense.
If you haven’t done so yet, consider building an IT cybersecurity strategy that includes file encryption; it’s me. Some IT teams use free OpenPGP tools to achieve file security. Others opt for a centralized managed file security. Others GoAnywhere MFT protect their data with more features and benefits surrounding the process.
Your unique business needs can help determine which method is best for your file transfer and security needs.

Why does encryption matter?
Several factors must be considered when choosing which encryption standards to implement at your organizing. Before choosing an encryption standard to use, ask the following queso’s:
• How censive is the data being exchanged?
• How will the data be transmitted (FTP, email, HTTP, etc.)?
• Are large files, which should be compressed, being exchanged?
• Should the actual files be encrypted (before transmission) or should the connector itself be encrypted?
• What encryption standards do your trading partners support?
A trading partner may lately dictate the encryption standards which they support. For instance, many banking instants require that customers encrypt files using the OpenPGP encryption standard.
1. Low sensitivity, password protection needed
You need to send your price list file to your customers over email. You want it to be easy to for these customers to open the file. While this price list information is not extremely sensitive, you would like to at least password-protect it.
Recommendation:
ZIP with AES encryption
2. Highly sensitive banking information, FTP connection
You need to send your company’s payroll direct-deposit information to the bank. This is considered highly sensitive information. Your bank wants you to send this information over a standard FTP connection.
Recommendation:
OpenPGP
3. Authentication with password or public key, FTP Connection
Your trading partner wants to exchange information with you over a secure FTP connection. This trading partner also wants to authenticate your company with a password or public key.
Recommendation:
SFTP
Why does encryption matter?
4. Authentication with signed certificate, FTP connection
Your trading partner wants to exchange information with you over a secure FTP connection. This trading partner also wants to authenticate your company with a signed corticate.
Recommendation:
FTPS (FTP over SSL)
5. Large, sensitive files, FTP or email distribution
You need to send purchase orders to your vendors, which you consider fairly sensitive data. The files can be rather large in size and should be compressed before being sent. The purchase orders could be sent over standard FTP connections or via email.
Recommendation:
ZIP with AES Encryption, Secure Mail, or Open PGP
6. EDI files requiring confirmation
You need to send EDI information securely to a trading partner and you also need confirmation that they received the exact document(s) you sent them.
Recommendation:
AS2 (S/MIME over HTTP/S) or AS4
GoAnywhere MFT
GoAnywhere MFT is a Managed File Transfer solution developed by Fortra that automates and secures file transfers using a centralised, enterprise-level approach.
GoAnywhere provides a safe and secure way to automatically transfer information inside and outside your organisation. File transfers and related business processes will be streamlined with GoAnywhere without your team needing any prior programming or scripting knowledge.
GoAnywhere MFT is flexible, scalable, highly available and offers rapid, controllable upgrades. Running GoAnywhere in a hybrid cloud environment can help your business reduce costs and protect key business data in the event of an unexpected outage or disaster.
To find out more about GoAnywhere MFT, request a dedicated 15-minute chat with one of our experts.
About BlueFinch-ESBD
Since 2011, BlueFinch-ESBD has specialised in Managed File Transfer (MFT) and has deployed over 1,000 solutions in Europe. Our customers come from a wide range of sectors such as banking, insurance, retail, industry, NGOs, finance, transport, logistics and government, some of whom are world-renowned companies that we have been supporting for a long time.
Our team of experienced and certified technical specialists guides organisations through their file transfer and integration projects, delivering optimised, high-performance solutions tailored to their environments and needs. We pride ourselves on maintaining a close, high-quality relationship with our customers, providing them with a high level of service from initial sales contact through to technical support.
We support our customers throughout the lifecycle of their MFT deployment by offering high value-added professional services to support their growth strategy, as well as managed services, a catalogue of MFT training courses and technical support based in France and the Netherlands.
- FRANCE : +33(0)9 70 75 61 13
- NETHERLANDS : +31(0)8 82 58 33 46
- sales@bluefinch-esbd.com
- www.bluefinch-esbd.com